Renal Disease and Analgesic Choice
TYLENOL® does not compromise renal function in patients with existing kidney dysfunction when taken at recommended doses1,2
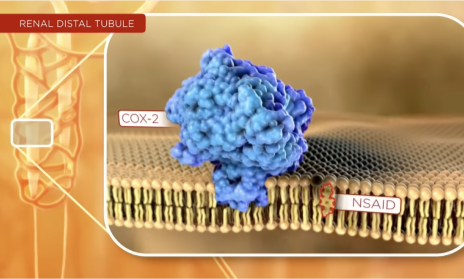
TYLENOL® does not impact the COX pathways that affect kidney function the way that NSAIDs can
Two cyclooxygenase (COX) pathways affect kidney function—COX-1 and COX-2—and NSAIDs can impact both3,4
In kidneys with some degree of dysfunction, NSAIDs’ COX inhibition may4:
Compromise renal function
Promote sodium and fluid retention
The National Kidney Foundation has identified acetaminophen as the pain reliever of choice for occasional use in patients with underlying renal disease5
*When used as directed.
†Maximum strength lidocaine without a prescription.
Patient populations where renal risks may be a concern
NSAIDs may precipitate acute renal failure in the elderly and in some patients with4:
Preexisting renal insufficiency
Hypertension
Congestive heart failure
Diabetes
Cirrhosis
Sepsis
Renal Dysfunction Risk
Watch how NSAIDs’ COX inhibition may compromise renal function4

Order practice resources
Get complimentary samples and coupons, condition-focused patient education resources, and more.
NSAIDs=nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; OTC=over-the-counter
References
1. Prescott LF, Speirs GC, Critchley JA, Temple RM, Winney RJ. Paracetamol disposition and metabolite kinetics in patients with chronic renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;36(3):291-297.
2. Martin U, Temple RM, Winney RJ, Prescott LF. The disposition of paracetamol and the accumulation of its glucuronide and sulphate conjugates during multiple dosing in patients with chronic renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;41(1):43-46.
3. Weir MR. Renal effects of nonselective NSAIDs and coxibs. Cleve Clin J Med. 2002;69 Suppl 1:SI53-SI58.
4. Bugge JF. Renal effects and complications of NSAIDs for routine post-operative pain relief: increased awareness of a real problem is needed. Baillieres Clin Anaesthesiol. 1995;9(3):483-492.
5. Henrich WL, Agodoa LE, Barrett B, et al. Analgesics and the kidney: summary and recommendations to the Scientific Advisory Board of the National Kidney Foundation from an ad hoc committee of the National Kidney Foundation. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996;27(1):162-165.
