Multimodal Pain Management
Consider both pharmacologic + nonpharmacologic modalities as part of your recommended pain management strategy
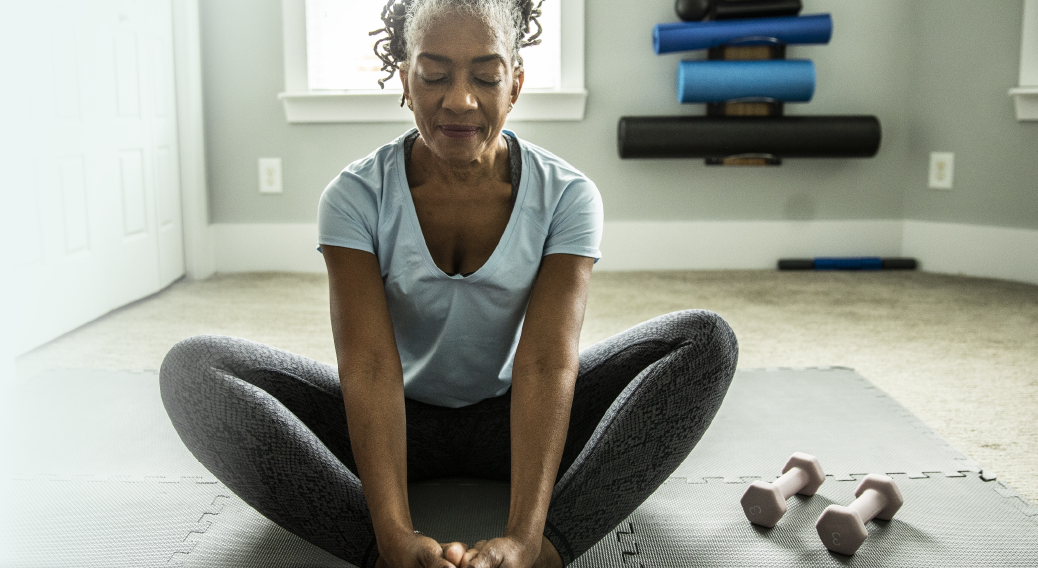

A combined approach can lead to effective pain relief
Recommend TYLENOL® as a foundation of an individualized multimodal plan
Multimodal pain management uses a combination of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic approaches to complement one another1
TYLENOL® provides powerful pain relief, whether used on its own or as part of a well-rounded, individualized multimodal plan
TYLENOL® has an outstanding safety profile when used as directed
Here are examples of multimodal techniques that can reduce stress and address other factors that may exacerbate pain.
*When used as directed.
†Maximum strength lidocaine without a prescription.
FOR BACK PAIN
For patients with back pain, experts recommend pharmacologic interventions combined with lifestyle changes, physiotherapy, and nonpharmacologic methods.2 Recommend TYLENOL® in addition to techniques like these:
Ice for the first 48 hours, 5 to 10 minutes at a time
Heating pad or hot shower after 48 hours
Gentle yoga1
Physical therapy, massage, or chiropractic adjustment3
Encourage lifestyle changes
In a study, patients with back pain who changed their lifestyle—such as reducing smoking and alcohol and increasing physical activity—achieved better results in nonpharmacologic treatment and experienced higher pain alleviation compared with the patients treated by medications only.2
*When used as directed.
†Maximum strength lidocaine without a prescription.
FOR MUSCLE ACHES, STRAINS, AND SPRAINS
Muscle, tendon, and ligament pain can interfere with patients’ exercise routines, sometimes causing a decrease in motivation and overall fitness. To get patients moving again, recommend TYLENOL® in addition to techniques such as:
RICE: rest, ice, compression, and elevation1
Stretching
When appropriate, topical analgesics (such as BENGAY®)4
Prevention is key
Counsel your patients to take these preventative measures in order to avoid muscle aches and pains:
Stretch before and after exercise
Do a few minutes of mild warm-up and cool-down before and after vigorous exercise
Increase the level of difficulty in small increments, not big leaps
Drink lots of fluids before, during, and after exercise
At work, vary activities as much as possible, and try to stretch at least once every hour
*When used as directed.
†Maximum strength lidocaine without a prescription.

FOR HEADACHE
Headaches are common and often debilitating, with significant socioeconomic and personal impacts.5 Patients who take OTC pain relievers more than 3 times a week on a regular basis can experience medication-overuse headaches.6 Screen patients for overuse, and counsel them to combine pain relievers with nonpharmacologic treatments such as:
Hot shower or bath; heating pad applied to head and neck muscles
Ice pack or cool compress on the forehead
Gentle massage of the temples, scalp, neck, and shoulders7
Relaxation techniques: deep breathing, guided imagery, or progressive muscle relaxation7,8
Walking
Help patients cope
The diagnosis and treatment of chronic headaches is not always quick, and this can cause emotional stress in patients. Suggest measures that can help patients regain a sense of control over their situation,6 such as getting enough sleep, eating regularly scheduled meals, or joining a headache support group.
*When used as directed.
†Maximum strength lidocaine without a prescription.
FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS
Experts recommend using multiple treatment methods to reduce pain and improve joint function in patients with osteoarthritis.9 In one study, TYLENOL® has demonstrated analgesic efficacy in osteoarthritis, even when inflammation was present—making it an important part of a well-rounded pain management plan that can also include10:
Weight loss: losing 1 pound takes 4 pounds of pressure off knees11
Exercise12
When appropriate, topical analgesics (such as MOTRIN® Arthritis Pain Gel)4
Joint protection through proper sitting, standing, and lifting techniques
Help patients reduce OA pain with our Keep Moving® program. The free online program includes actionable ways for OA patients to lose weight, exercise, and protect joints.
*When used as directed.
†Maximum strength lidocaine without a prescription.
Psychological factors

Research shows that most patients with chronic pain experience emotional distress—most commonly, feelings of anxiety and depression. These negative moods may affect biological and behavioral responses, producing a vicious cycle that can lead to disability and reduced quality of life.13
Since early identification of psychosocial problems may help prevent pain from becoming chronic, it’s important to ask patients how they’re feeling and, when necessary, refer them to an appropriately trained specialist for further evaluation.14
OTC=over-the-counter
*When used as directed.
†Maximum strength lidocaine without a prescription.
References
1. Pain Management Best Practices Inter-Agency Task Force. Pain Management Best Practices Inter-Agency Task Force Report: Updates, Gaps, Inconsistencies, and Recommendations. US Dept of Health and Human Services. May 9, 2019. Accessed March 22, 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/pain-mgmt-best-practices-draft-final-report-05062019.pdf
2. Ondrejkovicova A, Petrovics G, Svitkova K, Balogh V. Is non-pharmacological treatment an effective option for chronic low back pain? Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2017;38(3):169-172.
3. Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, et al. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(7):514-530.
4. Derry S, Wiffen PJ, Kalso EA, et al. Topical analgesics for acute and chronic pain in adults–an overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;5(5):CD008609.
5. Lacerenza MR, Schoss F, Grazzi L. The multimodal treatment in headaches. J Headache Pain. 2015;16(Suppl 1):A47.
6. Headache. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Accessed March 19, 2023. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/headache#3138
7. Tension-type headaches: self-care measures for relief. Mayo Clinic. October 1, 2022. Accessed March 19, 2023. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tension-headache/in-depth/headaches/art-20047631?pg=2
8. Tame your tension headaches naturally. Cleveland Clinic. March 11, 2020. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/tame-your-tension-headaches-naturally/
9. Brander V. Changing the treatment paradigm: moving to multimodal and integrated osteoarthritis disease management. J Fam Pract. 2011;60(11, suppl 2):S41-S47.
10. Bradley JD, Brandt KD, Katz BP, Kalasinski LA, Ryan SI. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis: relationship of clinical features of joint inflammation to the response to a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug or pure analgesic. J Rheumatol. 1992;19(12):1950-1954.
11. Messier SP, Gutekunst DJ, Davis C, DeVita P. Weight loss reduces knee-joint loads in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(7):2026-2032.
12. Penninx BW, Messier SP, Rejeski WJ, et al. Physical exercise and the prevention of disability in activities of daily living in older persons with osteoarthritis. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(19):2309-2316.
13. Shuchang H, Mingwei H, Hongxiao J, et al. Emotional and neurobehavioural status in chronic pain patients. Pain Res Manag. 2011;16(1):41-43.
14. Nadler SF. Nonpharmacologic management of pain. J Am Osteopath J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2004;(11 suppl 8):S6-S12.